The United States Army is the largest and oldest service of the military. This land service branch of the US Armed Forces provides the nation’s fighting force, safeguarding territories, resources, and people.
As of 2021, the U.S. Army has a total of 485,000 active-duty soldiers, 189,500 reserve soldiers, and 336,00 national guards. These service members each have their own ranks and designation, identifiable through the insignia worn on the shoulder or collar of their uniforms. Take a look at the complete list of the U.S. Army ranks, categorized by their insignia.
Enlisted Ranks
Enlisted ranks are responsible for 83% of the U.S. military. They carry out orders for military missions, humanitarian aid, and disaster relief. Enlisted Ranks account for more than 180,000 people applying for the military annually.
Under enlisted ranks are junior enlisted ranks, non-commissioned officer ranks, senior non-commissioned officer ranks, and the Sergeant Major of the Army. Get to know the soldiers and their insignia under Enlisted Ranks.
Junior Enlisted Ranks (E-1 to E-3)
Junior enlisted ranks have the lowest rank under Enlisted Ranks. They are either under training or on their initial assignment. Soldiers under junior enlisted ranks are recruits, privates, and army specialists.
Private (E-1)
Privates (PVT) or recruits are soldiers who have just joined the U.S. Army. They undergo Basic Combat Training or boot camp over a ten-week period that trains them to be full-fledged soldiers. They have no rank insignia at this level. The pay grade of PVT soldiers is E-1.
Private Second Class (E-2)

Private Second Class personnel (PV2) are soldiers who completed basic training. They are the most junior members of the Army to have a rank insignia. The role of PV2s is to learn new knowledge and hone their skills from the boot camp. The pay grade for PV2 soldiers is E-2.
Private First Class (E-3)

Private First Class (PFC) soldiers are either promoted enlisted personnel from PV2 or entered the Army with prior military experience. At this rank, PFCs move forward from being an apprentice to developing leadership skills of their own. The pay grade of PFCs is E-3.
Specialist (E-4)

Specialists (SPC) have the highest rank among junior enlisted ranks. They can lead enlisted soldiers, especially PV1. Aside from promotion, soldiers can rank as SPCs if they have a bachelor’s degree or have specialized military skills. The pay grade of SPCs is E-4.
Non-commissioned Officer Ranks (E-4 to E-6)
Non-commissioned officer ranks (NCOs) or junior NCOs are mid-level enlisted personnel tasked with the care, training, education, and readiness of soldiers in the U.S. Army. They lead other junior enlisted rank soldiers in the military rank structure.
Corporal (E-4)

Corporals (CPL) are responsible for the soldiers’ appearance, cleanliness, and individual training in the military occupation specialty (MOS). They are also referred to as junior non-commissioned officers. CPLs have the same pay grade as SPCs at E-4.
Sergeant (E-5)

Sergeants (SGT) lead a team of four soldiers in their command. They are often the lowest-level NCO leaders for junior enlisted ranks, leading them in individual training, personal appearance, cleanliness, and MOS competency. The pay grade for SGTs is E-5.
Staff Sergeant (E-6)

Staff Sergeants (SSG) lead a squad or section comprising 2-3 teams of 8-16 soldiers. Under their command is one or more sergeants, which help them train, develop, and enforce MOS skills to soldiers for unit mission operations. The pay grade of SSGs is E-6.
Senior non-commissioned officers
Senior non-commissioned officers (SNCOs) hold the highest responsibilities among NCO ranks. Under this command is sergeant first class, master sergeant, first sergeant, sergeant major, command sergeant major, and Sergeant Major of the Army.
Sergeant First Class (Platoon Sergeant) (E-7)

Sergeant First Class (SFC) soldiers are the first level of senior NCOs. They assist the platoon leader in training and caring for soldiers and staff sergeants. Being the second in command in a platoon, they can also be called a Platoon Sergeant. The pay grade of SFCs is E-7.
Master Sergeant (E-8)

Master Sergeants (MSG) are the principal NCOs of a battalion, brigade, or higher level. They are subject matter experts and can hold other positions in the Army at the same time. MSGs and first sergeants may have similar pay grades at E-8 but not in authority or responsibilities.
First Sergeant (E-8)

First Sergeants (1SG) are the lifeblood of the Army, responsible for holding formations, instructing platoon sergeants, and assisting all enlisted members. The senior NCO rank assists in company-level command of 60-200 soldiers. As mentioned, the pay grade of 1Gs is E-8.
Sergent Major (E-9)

Sergeant Major (SGM) soldiers are subject matter experts who serve as policy development advisors. They have a wide sphere of influence, especially in battalion-level command of 300-1,000 soldiers. The pay grade SGMs is E-9—the highest among Enlisted Ranks.
Command Sergeant Major (E-9)

Command Sergeant Major (CSM) members give professional recommendations, oversee policy and standards implementation, and train soldiers under enlisted ranks. They also assist in brigade-level commands of 1,500-3,200 soldiers. The pay grade of CSMs is E-9.
Sergeant Major of the Army (E-9S)

The Sergeant Major of the Army (SMA) is the highest role in Enlisted Ranks of the Army. There’s only one SMA at a time, addressing the most important issues among enlisted soldiers and acting as the eyes and ears of the Chief of Staff. The pay grade of the SMA is E-9S.
Officer Ranks
Officer ranks are managers, responsible for planning missions, giving orders, and assigning different tasks for operations. While the number of soldiers in Officer Ranks is relatively smaller, they play an important role in organizing enlisted soldiers, operating federal government equipment such as aircraft, ships, and armored vehicles, and providing professional services for medical, legal, and more.
Every year, 20,000 people apply for the Officer Ranks. Under this rank are warrant officers, company grade officers, field grade officers, and general officers. See the Officer Ranks soldiers and their rank insignia.
Warrant Officers
Warrant officers are equipped with technical expertise, helping them serve as combat leaders, trainers, and advisors. They specialize in different military capabilities and technologies that maintain, operate, and integrate systems and equipment of the U.S. Army.
Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)

Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) is the most junior of the warrant officers. They use their technical expertise for tactical training, carrying out various duties, serving as secretaries, and acting as technical leaders and advisers. The pay grade of WO1 soldiers is W-1.
Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2)

Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) is commissioned by the President of the United States to provide technical expertise in their chosen fields. They serve as intermediate-level experts with duties and responsibilities at the battalion level. The pay grade of CW2 officers is W-2.
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3)
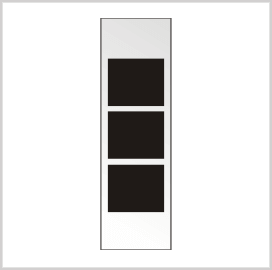
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) ranks higher than CW2. They have advanced-level technical and tactical expertise, providing support, guidance, resources, and counsel. CW3 handles responsibilities at the brigade level. The pay grade of CW3 soldiers is W-3.
Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4)
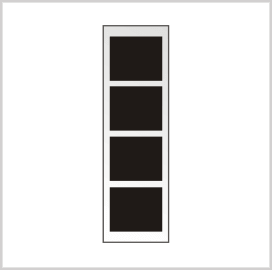
Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) is a senior-level expert for various military units, including battalions, brigades, corps, divisions, and echelons. One of their key roles is to provide special mentorship to other lower-ranked warrant officers. The pay grade of CW4 members is W-4.
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5)
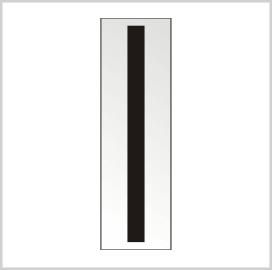
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) has complete mastery of the tactical aspects of their fields. Having the highest rank among warrant officers, they lead development opportunities, give mentorship, and offer advice to command operations. The pay grade of CW5 officers is W-5.
Company Grade Commissioned Officers
Company-grade officers hold the most junior roles among commissioned officers in the U.S. Army. They handle troops, ranging from platoon to company level. Under company grade commissioned officers are second lieutenants, first lieutenants, and captains.
Second Lieutenant (O-1)
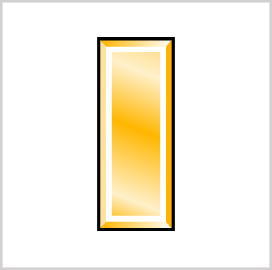
Second Lieutenants (2LT) are the most junior rank for commissioned officers. While they’re often considered entry-level, they lead a platoon of 16-44 soldiers and a platoon sergeant as the second in command. The pay grade of 2LTs is O-1.
First Lieutenant (O-2)

First Lieutenant (1LT), also referred to as a senior lieutenant, has been in service for 18-24 months. On top of leading specialized weapons platoons, they head indirect fire computation centers. 1LT may also lead a company of up to 140 members. The pay grade of 1LT is O-2.
Captain (O-3)
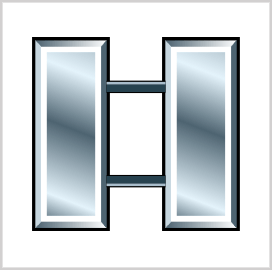
Captains (CPT) serve as unit commanders for a company composed of 3-5 platoons or 60-200 soldiers. They work with principal NCOs, leading skills instruction at Army combat training centers. CPTs are also often chosen as staff officers of a battalion. The pay grade of CPTs is O-3.
Field Grade Commissioned Officers
Field grade officers, also called mid-grade officers, play a huge leadership role in the U.S. Army. They comprise 36% of the Office Ranks and hold considerable responsibilities, such as advisors, instructors, and leaders of most military operations.
Major (O-4)
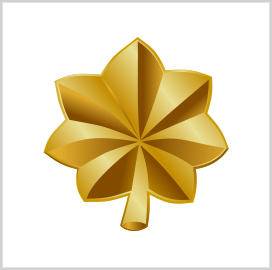
Majors (MAJ) serve as the task force commander and staff officer at a brigade-level unit composed of 1,500-3,000 soldiers. They play a key role in the Army’s personnel, logistical, and operational missions. The pay grade of MAJs is O-4.
Lieutenant Colonel (O-5)
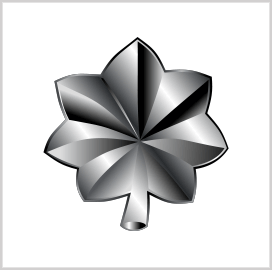
Lieutenant Colonels (LTC) oversee battalion-level units of 300-1,000 soldiers. They work closely with command sergeant majors as the principal NCO assistants for combat arms, combat support, and combat service support. The pay grade of LTCs is O-5.
Colonel (O-6)

Colonels (COL) are responsible for brigade-level operations, composed of 3 or more battalions or 1,500-3,200 soldiers. They are usually selected as chiefs for divisional-level staff agencies. COLs have a unique rank insignia, reflecting an eagle. The pay grade of COLs is O-6.
General Commissioned Officers
General officers have the most military powers in the United States Army. They operate on a star rank structure— the higher number of stars, the higher the rank. Under general officers are brigadier general, major general, lieutenant colonel, general, and General of the Army.
Brigadier General (O-7)
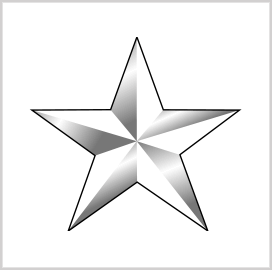
Brigadier General (BG) serves as a deputy commander of a major general. Together, they oversee division-level units composed of 3-4 brigades or 16,000 soldiers. BGs are responsible for planning and coordinating personnel in a division. The pay grade of BGs is O-7.
Major General (O-8)

Major Generals (MG) have a two-star rank insignia, showing their lead command at division-level units of 10,000-16,000 soldiers. They perform tactical operations for sustained battles and engagements of the U.S. Army. The pay grade of MGs is O-8.
Lieutenant General (O-9)

Lieutenant Generals (LTG) lead one of the biggest units in the U.S. Army. They lead corps, comprising 2-5 divisions or 20,000-40,000 soldiers. LTGs are responsible for command, control, and logistical support, often assisted by a CSM. The pay grade of LTGs is O-9.
General (O-10)

Generals (GEN) have the most seniority among general commissioned officers. With over 30 years in service, they command field army, army group, and army region, composed of up to 1 million personnel. The rank insignia of GEN is made up of four stars, with a pay grade of O-10.
General of the Army
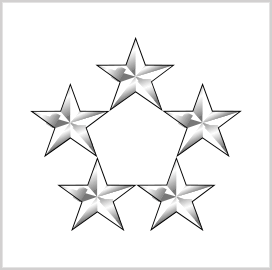
General of the Army (GOA) is reserved only during wartime. They serve as the commanding officer to create, implement, and order strategies for other lower rank soldiers. The last GOA appointment was during World War II and Korean War, including officers such as Douglas MacArthur, Dwight D. Eisenhower, and Omar Bradley.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the U.S. Army?

The Army was founded in 1775 and was established even before the founding of the United States. It is one of the six U.S. military branches, completing the Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The U.S. Department of the Army receives the biggest share of the Department of Defense’s budget for 2022.
What is the U.S. Army rank insignia?
An insignia is an official emblem that symbolizes the ranking of soldiers in the U.S. Army. It reflects the soldier’s position, leadership responsibilities, and operations. All military ranks across the branches of the U.S. Armed Forces have their respective insignia.
What is the rank structure of the U.S. Army?
The U.S. Army command structure can be divided into enlisted ranks and officer ranks. Enlisted Ranks account for most of the U.S. Army, serving as the backbone of military operations. On the other hand, Officer Ranks manage personnel, assign orders, and carry out mission operations.
United States Army: “This We’ll Defend”
Regardless of the United States Army ranks, soldiers uphold the motto and values to “defend the nation, protect vital national interests, and fulfill national military responsibilities.” Salute them for their undying duty and service to the people.


